All about Bangladeshi Culture
and Multi-culture
Cultures of Bangladesh and influence of multi-culture on our lives
About
- By Rodoshi Tahrin.

Content
Bangladeshi Culture:
Bangladesh has a rich, diverse culture. Its deeply rooted heritage is thoroughly reflected in its architecture, dance, literature, music, painting and clothing. The Bengal Renaissance of the 18th early 19th centuries, noted Bengali writers, saints, authors, scientists, researchers, thinkers, music composers, painters, film-makers have played a significant role in the development of Bengali culture.
History of Bangladesh:
 The borders of modern Bangladesh were established with the separation of Bengal and India in August 1947, when the region became East Pakistan as a part of the newly formed State of Pakistan following the end of British rule in the region. Pakistan and Bangladesh are both South Asian Muslim-majority countries. Following the end of the British Raj, the two countries formed a single state for 24 years. The Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971 resulted in the secession of East Pakistan as the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The war began after the Pakistani military junta based in West Pakistan launched Operation Searchlight against the people of East Pakistan on the night of 25 March 1971. The next day, on 26 March, 1971, the War for Independence of Bangladesh was declared, which is now celebrated as Independence Day. After 9 months of war, Bangladesh defeated Pakistan in 16 December, 1971, and East Pakistan became independent and officially got its name, Bangladesh. This day is known as Victory Day.
The borders of modern Bangladesh were established with the separation of Bengal and India in August 1947, when the region became East Pakistan as a part of the newly formed State of Pakistan following the end of British rule in the region. Pakistan and Bangladesh are both South Asian Muslim-majority countries. Following the end of the British Raj, the two countries formed a single state for 24 years. The Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971 resulted in the secession of East Pakistan as the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The war began after the Pakistani military junta based in West Pakistan launched Operation Searchlight against the people of East Pakistan on the night of 25 March 1971. The next day, on 26 March, 1971, the War for Independence of Bangladesh was declared, which is now celebrated as Independence Day. After 9 months of war, Bangladesh defeated Pakistan in 16 December, 1971, and East Pakistan became independent and officially got its name, Bangladesh. This day is known as Victory Day.
Language Day:
Before the liberation war, Bangladesh was a part of Pakistan. In 1952, the Central Pakistani Government made a decision to make Urdu the national language of Pakistan. The situation got worse when it was declared that only and only Urdu will be the national language of both East and West Pakistan. But the majority of East Pakistan spoke in Bangla and did not accept Urdu to be their national language. Defying this, the students of the University of Dhaka and Dhaka Medical College and other political activists started a procession on 21 February 1952. Near the current Dhaka Medical College Hospital, police fired on the protesters and numerous people, including Abdus Salam, Rafiq Uddin Ahmed, Sofiur Rahman, Abul Barkat, and Abdul Jabbar died. The movement spread to the whole of East Pakistan and the whole province came to a standstill. Afterward, the Government of Pakistan relented and gave Bengali equal status as a national language. This movement is thought to have sown the seeds for the independence movement which resulted in the liberation of Bangladesh in 1971. To commemorate this movement, Shaheed Minar, a solemn and symbolic sculpture, was erected in the place of the massacre. This day was officially declared as The Mother Language Day and Shaheed Dibas. Later, UNESCO decided to observe 21 February as International Mother Language Day.

Cultures of Bangladesh
Language:
The mother language of Bangladesh is called “Bangla”. Bangla was officially declared as the mother language of Bangladesh in 21 February. It mainly occurred because many people, especially students from Dhaka university did a procession as they didn’t accept Urdu as their mother language. During the procession, many people lost their lives. Because of this, Bangla was declared as the mother language of Bangladesh.

Dresses:
Bangladesh is home to a diverse range of traditional clothing which is still worn by people in their everyday life. Weaving the fabric for these dresses is a traditional art in Bangladesh. Some of the common dresses of Bangladeshi culture includes:
Men- Pajama, Panjabi, Lungi, Fotua etc.
Women- Shari, salwar kameez.

Foods:
Bangladesh is famous for its distinctive culinary tradition, delicious food, snacks, and savories. Some of the common foods of Bangladesh includes: Steamed rice, served with various vegetables, curry, thick lentil soups, pulse, egg, fish and meat, chicken, mutton, beef, duck etc. Some of the sweets includes- rasgulla, shondesh, rasmalai, Gulab jam, kalo jam, and chom-chom, jalebis, and laddus. Rice is the main food in Bangladesh. Also, fish is a regular food in Bangladesh. The national fish of Bangladesh is Hilsha (known as Ilish). Many types of fruits are also there. The national fruit of Bangladesh is Jackfruit.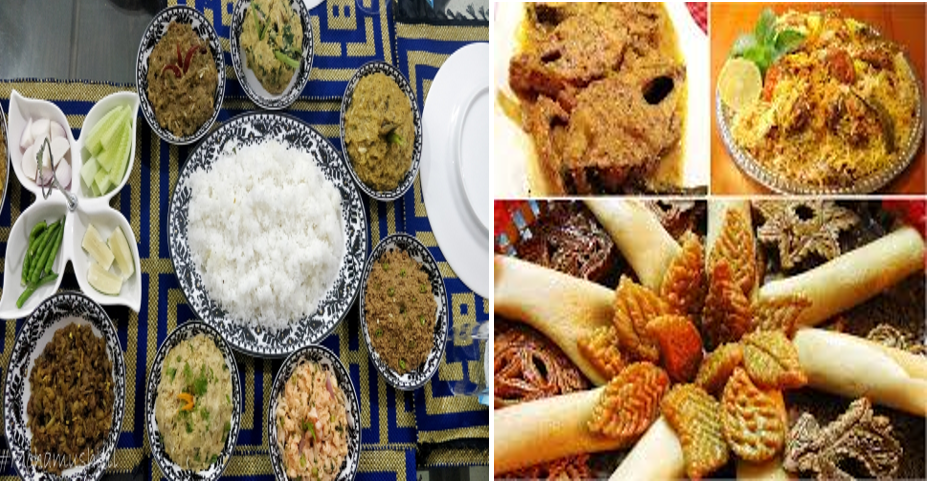
Religion:
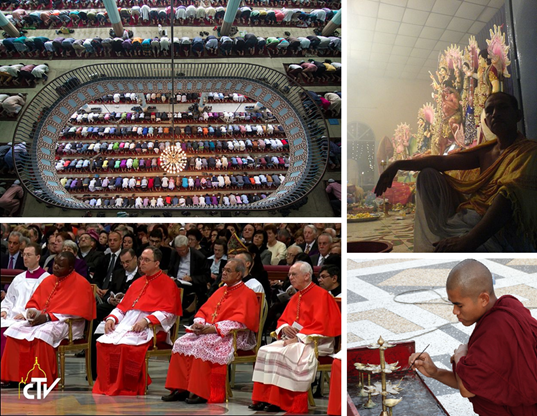
Bangladesh is a Muslim-majority country. Muslims constitute around 90% of the population in Bangladesh while Hindus and Buddhists are the most significant minorities of the country. People of different religions perform their religious rituals with festivity in Bangladesh. Also the government of Bangladesh declared Public Holidays during important festivals, like- Eid-ul-Fitre, Eid-ul-Adha, Puja, Christmas, Buddha Purnima etc.

Tribes of Bangladesh:
There are many tribes of Bangladesh. It includes- Chakma, Garo, Khasi, Jaintia, Marma, Santhal, Manipuri, Tripuri, Tanchangya, Mru, Mandi, Kuki, Bawm, Oraon, Khiang, Chak, Dhanuk, Munda etc. These people also have their own respective festivals.

Celebrations and Festivals:
There are several festivals celebrated in Bangladesh. One of the common festivals in Bangladesh is Pohela Boishakh. It is the Bangla new year which is celebrated in the first day of the first month of Bangla calendar, Boishakh, like it is celebrated in English year as Christmas. Also, 21 February is observed as Shaheed Dibas and International Mother Language Day, 26 March is observed as Independence Day and 16 December is celebrated as Victory Day. Also, there is a harvest festival celebrated in Bangladesh, called Nobanno. Other religious festivals are also celebrated as Eid, Puja, Christmas, Buddha Purnima etc.
Music and Dance:
The music dance styles of Bangladesh may be divided into three categories: classical, folk, modern. As Bangladesh was a part of Pakistan, the classical style has been influenced by other prevalent classical forms of music dances of the Indian subcontinent, accordingly, show some influenced dance forms like Bharatanatyam Kathak. But Bangladesh has developed its own distinct dancing styles. Bangladesh has a rich tradition of folk songs, with lyrics rooted in vibrant tradition. The most widespread folk songs music traditions include Bhatiali, Baul, Marfati, Murshidi, Bhawaiya. Lyricists like Lalon Shah, Hason Raja, Kangal Harinath, Romesh Shill, Abbas Uddin, many other lyricists have developed the tradition of folk songs of Bangladesh.
Several musical instruments are used in Bangladesh. Major musical instruments used are the bamboo flute (known as Bashi), drums (tabla, dhol), ektara (a single-stringed instrument), dotara (a four-stringed instrument) etc.

Sports:
Kabaddi is the national sport in Bangladesh. Kabaddi is a contact team sport played between two teams of seven players each. The objective of the game is for a single player on offense, referred to as a "raider", to run into the opposing team's half of a court, tag out as many of their defenders as possible, and return to their own half of the court, all without being tackled by the defenders, and in a single breath. Other traditional sports like Athletics, Swimming, Boli Khela, Lathi Khela are mostly played in the rural areas.

Weddings:
The traditional wedding of Bangladesh has 4 parts. Like- Mehdi Shondha, Holud, Biye(wedding) and Bou Bhaat(reception). Weddings in Bangladesh take several days and are very elaborate. Typically, wedding customs in Bangladesh take three days from engagement to post wedding rituals.

Art and Architecture:
The architecture of Bangladesh has a long history and is rooted in Bangladesh's culture, religion and history. Some of the architectures of Bangladesh includes- Lalbagh fort, Ahsan Manzil, Shat Gombuj Masjid, Jatio Sangsad Bhaban etc. Bangladeshi art has a perennial history which originated more than two thousand years ago and is practiced even to this date. Among the various forms of Bangladeshi art, photography, architecture, sculpture and painting are the most notable.

Multi-culture:
Multi-culture is the practice of several or multiple cultures in a society or country. Multi-culture is something that influences our lifestyle. It mainly occurs because of the migration of people in different places overtime. In history, people migrated and is still migrating in many areas around the world, for purposes including employment, higher education, colonization, exploration etc. These migrations eventually lead to multi-culture as well as cultural diffusion. Cultural diffusion is when a culture is mixed with another culture so much that it eventually is considered as a part of the same culture. Multi-culture and cultural diffusion can be observed almost everywhere in the modern world. Even Bangladesh is a multi-cultural country. In Bangladesh, many cultures are practiced. Like-
Foods:
Due to the migration of people of various cultures, Bangladeshis eventually adopted their foods, now in the present day, Food habits, includes eating foods such as sandwiches, tea, cake, burger, French fries etc. These foods are originated from other countries and other cultures.

Language:
Due to the British colonization, English became the international language or the leading language. In today’s world, English is spoken worldwide and is essential for many people to know. In Bangladesh, English is spoken by many people. Also, in Bangladesh, almost 38 different languages are spoken. Many schools and institutes are teaching new languages to help people in communicating in other countries, like French.

Dresses:
Due to British colonization and migration of people of different cultures, new dresses, cloth designs and fashion are introduced in Bangladesh. Like- due to multi-culture, different dresses are worn by Bangladeshis, including gowns, shirt, pant, jeans, bow tie etc. These types of dresses are commonly worn by many Bangladeshis, especially in Urban areas.

Religion:
In the present day, there are many religions practiced in Bangladesh. Muslims, Hindus, Buddhas, Christians are mostly common in Bangladesh. People of different religion also follows different culture, like the Muslims often learns Arabic because they need to read the Holy Quran (a holy book of the Muslims), which is in Arabic. Also, they celebrate festivals like Eid. Even their food habits are affected by their religion. Like for Muslims, eating pork or drinking alcohol is Haram (Forbidden). Their dresses are also based on their religion, like the Muslim women should wear Hijab and Burqas.

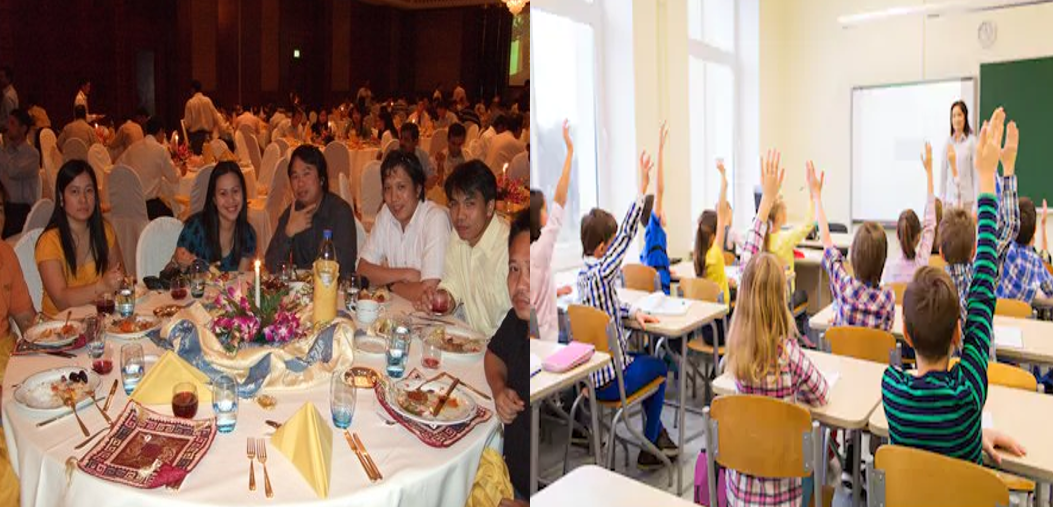
Celebration and Festival:
Due to multi-culture in Bangladesh, many people celebrate different festivals, like special days, like teacher’s day, Mother’s Day, Father’s Day, Thanksgiving Day etc., English New Year, birthday celebration etc. These were not in the culture of Bangladesh, but for migration of people of various cultures, these celebrations are now common in Bangladesh.

Music and Dance:
Because of Multi-culture, new types and style of dance, new genre of songs is now introduced and practiced in Bangladesh. Like- hip-hop, rock music, rap songs, contemporary dance etc. Also, many Bangladeshi singers now composes new songs of different genres in Bangla. Like Ayub Bachhu, Stoic Bliss etc.

Sports:
In Bangladesh, different types of games and sports are introduced and practiced, which were not there in the culture of Bangladesh. Like Cricket is a very popular game in Bangladesh, which was originated from England. Cricket is played a lot in Bangladesh. Even Bangladeshi cricketers played in the World Cup. Many other games are also there in Bangladesh, like Golf, football, Chess etc.

Art and Architecture:
Because of migration of people of different culture in Bangladesh, new style of art, designs, types of art, materials used in art and making architecture etc. were introduced in Bangladesh. like in Bangladesh, the designs of buildings and other architectures are adopted from the British people. When the British people colonized Bangladesh, they established many architectures and buildings. Their designs were very unique, which is now used by the Bangladeshis. Designs of buildings, roads, furniture, bridges etc. are mostly based on the concept of the designs made by British people.

Education and Manners:
The Bangladeshi people were not educated before. But when the British colonized Bangladesh, they gave education to the people of Bangladesh for doing business with them smoothly. This helped the Bangladeshi people to get education and prevent superstition. In the present day, many schools follow different ways of education that came from different countries and cultures, like- British curriculum, Cambridge curriculum etc.
British people also taught the Bangladeshis good manners. For this reason, the people are practicing good manners in Bangladesh, which came from different countries and cultures. Like- maintaining queuing, social etiquette, not to talk loudly, table etiquette etc.

Migration of different people in Bangladesh has had a huge impact on the culture of Bangladesh. Cultural diversification, cultural diffusion and multi-culture mainly occurred because of their migration. Although multi-culture in Bangladesh has had a positive impact on Bangladesh, it still impacted Bangladesh in a negative way. Mostly because of multi-culture, people are avoiding, ignoring or forgetting their own culture and tradition. Many people are not used to their culture because of multi-culture. Even many Bangladeshis don’t have enough knowledge about their own culture. lack of practicing own culture because of practicing of multi-culture can even lead to the abolishing of culture eventually.
That’s why people must be aware about it. Practicing multi-culture obviously helps people to adopt many things, which can benefit them to adjust with people of different cultures in the modern world. But people must also remember to practice their own culture. Culture of a person represents their motherland and their personality. Culture is reflected in our history, in our heritage and in how we express ideas and creativity. Our culture measures our quality of life, our vitality and the health of our society. Through our culture we develop a sense of belonging, personal and cognitive growth and the ability to empathize and relate to each other. That’s why, people must follow their own culture as well as practice multi-culture.



